Conversational LLM Powered Gen AI
Conversational AI For
Contact Center IntelligenceAutonomous AgentsCoaching and TrainingReal Time Assist
Enhancing CX Engagement
Empower your customer-facing teams with real-time and post-interaction intelligence. ODIO transforms conversations into data-driven opportunities using cutting-edge Generative AI.
Leading Enterprises into Future with Conversation AI
Revolutionize Customer Interactions with AI
ODIO Conversational LLM
Built on real conversational data, ODIO’s custom LLM delivers highly accurate, context-aware AI responses for seamless automation and agent assistance.
Key Features:
- Optimized for Conversations – Trained on real dialogue data for natural, human-like interactions.
- High Accuracy & Context Retention – AI understands intent, sentiment, and nuances for better engagement.
- Industry-Specific Adaptability – Tailored models for customer support, sales, banking, and training.
- Real-Time Assistance & Automation – Enhances virtual agents, agent coaching, and call analytics.
- Scalable & Secure – Enterprise-grade performance with robust data privacy controls.
Leverage ODIO’s advanced LLM to automate, analyze, and optimize every conversation with precision.
Contact Center Intelligence
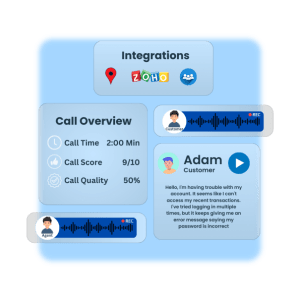
AI-driven QA for 100% of customer interactions—calls, chats, and emails—eliminating manual sampling.
Key Features:
AI-Powered Scoring – Unbiased, automated interaction assessments.
Custom Scorecards – Tailored QA evaluations for compliance & performance.
Generative AI Feedback – Instant coaching insights for agents.
Analytics Dashboards – Actionable reports for teams & managers.
Enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and drive superior customer experiences with ODIO’s Automated QA.
Intelligent Autonomous Agents
![]()
AI-powered chatbots and voice bots that automate customer interactions, enhancing efficiency and personalization.
Key Features:
- Conversational AI – Human-like responses with advanced NLP.
- Omnichannel Support – Seamless engagement across chat, voice, and messaging apps.
- Generative AI Adaptability – Continuous learning for improved interactions.
- Task Automation – Handles FAQs, scheduling, and transactions efficiently.
Boost customer experience, reduce costs, and streamline workflows with ODIO’s AI-driven Autonomous Agents.
Real-Time Assist for Agents & Supervisors
Empower agents with AI-driven guidance and enable supervisors with real-time insights to enhance customer interactions.
Key Features:
Instant Guidance – AI-powered prompts for accurate responses.
Live Monitoring – Supervisors track and support calls in real-time.
Dynamic Battlecards – Contextual information for better decision-making.
Sentiment & Compliance Alerts – Detect customer dissatisfaction and policy violations.
Direct Intervention – Supervisors provide live coaching when needed.
Improve agent performance, ensure compliance, and elevate customer experience with ODIO’s Real-Time Assist.
AI-Powered Agent Coaching
Train agents with voice-backed AI simulations that adapt to multiple customer personas for dynamic, real-time coaching.
Key Features:
- AI Roleplay – Simulated conversations with varied customer personas.
- Voice Interaction – Real-time coaching through AI-driven voice responses.
- Adaptive Learning – Personalized feedback based on agent performance.
- Behavior Analysis – Evaluates tone, sentiment, and response effectiveness.
- Performance Tracking – Insights to refine skills and enhance interactions.
Boost agent confidence and customer engagement with ODIO’s AI-Powered Coaching.
AI Powered Auto Phone Calls
Enhance customer engagement with human-like, Generative AI-driven virtual agents that automate complex interactions across industries like banking, hiring, training, and customer support.
Key Features:
- Human-Like Conversations – Natural, contextual AI interactions for seamless customer experiences.
- Industry-Specific Adaptability – Tailored solutions for banking, hiring, training, and more.
- Automated Call Handling – Manage inbound/outbound calls with real-time AI-driven responses.
- Lead Qualification & Engagement – AI-driven assessment of customer intent to prioritize leads.
- Appointment Scheduling & Reminders – Automate bookings and follow-ups to reduce no-shows.
- 24/7 Support & Assistance – AI agents available round-the-clock for uninterrupted service.
Drive efficiency, reduce operational costs, and scale customer interactions effortlessly with ODIO’s AI-Powered Virtual Agents
Multilingual AI for Global Conversations
ODIO’s AI-powered multilingual capabilities support both Indian and international languages, enabling seamless communication across diverse regions.
Key Features:
- Conversational Analytics – Accurately transcribe, analyze, and extract insights from multilingual interactions.
- AI Bots & Virtual Agents – Automate customer engagement in multiple languages for voice and chat.
- AI-Powered Training – Train agents with real-time coaching and simulations in their native language.
- Contextual Understanding – Ensures accuracy in intent recognition, sentiment analysis, and response generation.
Empower businesses with language-adaptive AI for enhanced customer experience and agent efficiency

Behind The Scenes @ ODIO
Advanced AI Technology
ODIO leverages custom-built LLMs, NLP, and high-accuracy speech recognition to power intelligent, secure, and multilingual automation across customer interactions.
How Our AI Works:
- Conversational AI Engine – Trained on real-world data for human-like, multilingual responses.
- Proprietary Speech Recognition (ASR) – High-accuracy transcriptions, even in noisy environments.
- AI-Driven Learning – Continuously improves intent detection, sentiment analysis, and predictions.
- Enterprise-Grade Security – End-to-end encryption and fraud detection for safe interactions.
With cutting-edge AI and real-time speech intelligence, ODIO delivers smarter automation, analytics, and agent assistance for superior customer experiences.
See ODIO in Action
Send your query or request a demo
Want to see how it works or Got any question, contact us
Master the art of risk management and “failproof” compliance with expert precision.














